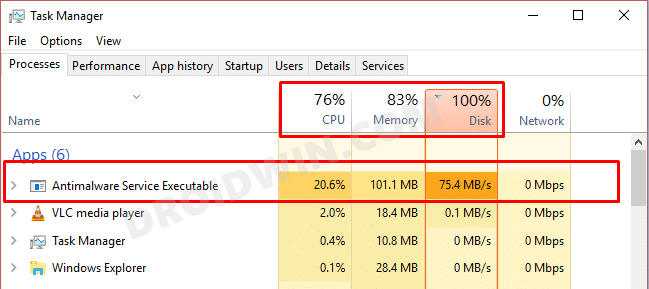
However, keeping its importance aside, it is notoriously infamous for consuming quite a lot of memory which ultimately leads to the slow-down of the entire system. Be it the CPU, Memory, or Disk Usage, it could negatively impact either of three or in some cases, even all these three components. So how to rectify this issue? Well, there exist a few handy workarounds that have been known to fix the Antimalware Service Executable High CPU or Memory usage. And in this guide, we will make you aware of just that. Follow along.
How to Fix Antimalware Service Executable High CPU/Memory Usage
Do note that there isn’t any universal fix as such. You will have to try out each of the below-mentioned tweaks and then verify which one works out best. So with that in mind, let’s get started.
FIX 1: Tweak Defender’s Scheduled Scan
To begin with, we will be changing the Windows Defender Scheduled scan and taking away some unwanted privileges from it as well. This will result in less consumption of the system resources by the Defender and in turn by the ASE. So proceed ahead with the instructions:
FIX 2: Remove Corrupt Windows Update Files
Microsoft releases cumulative updates that comes with a few enhancement for the Defender, along with the usual stability improvement and security enhancement to the OS. However, if the update is buggy or corrupt or gets disrupted during the download process, then it could spell out trouble for the Defender. Therefore, the best route forward is to delete these files. Here’s how it could be done:
FIX 3: Turn off Process Mitigation
Process Mitigation is in control of the Exploit Protection Service which turns is the major reason for the Windows Defender Bootloop issue. This happens when the Defender is trying to disable the activities of a particular app or folder but isn’t able to do so due to some restrictions being imposed on that content. So the Exploit Protection Service will force the Defender to retry disabling this activity, and this process will keep on going on in the backend. As a result, the Defender will end up in a bootloop, and in turn, will end consuming a considerable amount of system resources. To prevent this from happening, you will have to disable the Exploit Protection Service which could be carried out by turning off the Process Mitigation. So head over to the Start Menu and launch Command Prompt as an admin. Then execute the following command in that CMD window:
Once the command has been executed, it is recommended to restart your PC. Once it boots up, verify if the Antimalware Service Executable High CPU/Memory usage issue has been fixed or not.
FIX 4: Add Antimalware Service Executable to Defender Exclusion List
The next fix requires you to add the Antimalware Service Executable to Windows Defender’s whitelist. As a result, the Defender will no longer scan this service file, thereby reducing the load on the CPU.
FIX 5: Kill Antimalware Service Executable Process
Some users took this aggressive route of killing the Antimalware Service Executable Process and they did manage to rectify the underlying issue using this trick. Stopping this process would stop most of the associated Defender processes and upon a restart of your PC, they should be up and running again, this time with their fresh instances. So if you wish to try it out, then here’s what you need to do:
FIX 6: Disable True Color Service (For Dell users)
Some Dell users had found an interlink between the True Color (one of Dell’s bloatware apps) and the Antimalware services. Upon disabling the former, it turned out that the CPU load considerably decreased, even though the Antimalware service was still running. So it is recommended that the Dell users do give this tweak a try.
FIX 7: Disable Windows Defender
If none of the aforementioned methods managed to spell out success, then you should take the nuclear route and temporarily disable the Windows Defender app. There are two different methods through which this could be done: via Registry Editor and through Group Policy Editor. We have explained both these methods in-depth in this guide, do check it out: Shorter instructions are given below:
Group Policy: Launch the Group Policy Editor > Go to Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Windows Defender from the left menu bar > Now open the “Turn off Windows Defender” policy from the right-hand side and change its State to Enabled. Registry Editor: Launch Registry Editor > Go to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows Defender > Create DWORD (32-bit) Value inside the Windows Defender folder> Name it DisableAntiSpyware and enter 0 under Value Data. That’s it.
So with this, we round off the guide on how you could fix the Antimalware Service Executable High CPU/Memory usage issue. We have listed seven different methods for the same. Do let us know in the comments section which one worked out in your favor. Likewise, all your queries are welcomed in the comments below.
How to Fix Windows 11 High CPU and Disk UsageWindows 11 Start Menu Not Working: How to Fix [10+ Methods]Windows 11 Updates Failed Error: How to FixHow to Fix Internet or WiFi Not Working in Windows 11
About Chief Editor